Description
Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) are essential fats that play a crucial role in human health. They are termed “essential” because the body cannot synthesize them, requiring dietary intake for adequate levels. These fatty acids are vital for various bodily functions, including cardiovascular health, brain function, and inflammation regulation.
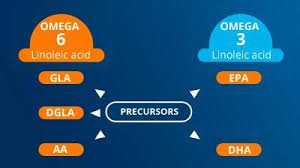
Types of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
There are three primary types of omega-3 fatty acids:
- Alpha-Linolenic Acid (ALA): Found in plant sources such as flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts, and canola oil, ALA is a short-chain omega-3 fatty acid. The body can convert ALA into the longer-chain omega-3s, EPA and DHA, but this conversion process is inefficient.
- Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA): Predominantly found in fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines, EPA is a long-chain omega-3 fatty acid known for its anti-inflammatory properties.
- Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA): Also found in fatty fish and algae, DHA is crucial for brain health, making up a significant portion of brain and retinal tissue.
Sources of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
To obtain sufficient omega-3 fatty acids, individuals can incorporate a variety of food sources into their diet:
- Fatty Fish: Salmon, mackerel, sardines, herring, and anchovies are among the richest sources of EPA and DHA.
- Plant Oils: Flaxseed oil, chia seed oil, and hemp oil are excellent sources of ALA.
- Nuts and Seeds: Walnuts, flaxseeds, chia seeds, and hemp seeds provide ALA.
- Algal Oil: A vegan source of DHA, algal oil supplements are derived from algae and are suitable for those avoiding fish products.
Health Benefits
Omega-3 fatty acids have been extensively studied for their health benefits, which include:
- Cardiovascular Health: Omega-3s are known to support heart health by lowering triglyceride levels, reducing blood pressure, and decreasing the risk of heart disease. They can also improve endothelial function and reduce inflammation, both of which are beneficial for cardiovascular health.
- Brain Health: DHA is particularly important for brain function and development. Studies suggest that adequate omega-3 intake may reduce the risk of cognitive decline and conditions like Alzheimer’s disease. Additionally, omega-3s may have a role in mood regulation and reducing symptoms of depression and anxiety.
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Omega-3 fatty acids can help reduce inflammation in the body, which is linked to various chronic conditions, including arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and autoimmune disorders.
- Eye Health: DHA is a major component of the retina. Adequate intake of omega-3s has been associated with a reduced risk of age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and dry eye syndrome.
- Pregnancy and Development: Omega-3s are crucial during pregnancy for fetal brain and eye development. Maternal intake of DHA has been linked to improved cognitive and visual development in infants.
Recommended Intake
The recommended intake of omega-3 fatty acids varies based on age, sex, and specific health conditions. Generally, health organizations suggest:
- ALA: About 1.1 grams per day for women and 1.6 grams for men.
- EPA and DHA: A combined total of 250-500 mg per day for general health, with higher amounts recommended for those with specific health conditions.
Supplementation
For individuals who may struggle to meet their omega-3 needs through diet alone, supplements are an option. Fish oil and algal oil supplements can provide concentrated doses of EPA and DHA. It’s essential to choose high-quality supplements that are free from contaminants, such as heavy metals.
Safety and Side Effects
Omega-3 supplementation is generally considered safe for most people. However, high doses may lead to side effects, including:
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Some individuals may experience nausea, diarrhea, or bloating.
- Increased Bleeding Risk: High doses of omega-3s can interfere with blood clotting, increasing the risk of bleeding, particularly in those on anticoagulant medications.
- Fishy Aftertaste or Burps: Some fish oil supplements can cause a fishy aftertaste or burps.
Conclusion
Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids are essential for maintaining overall health and well-being. Their numerous benefits, particularly for cardiovascular health, brain function, and inflammation management, make them a vital component of a balanced diet. Incorporating sources of omega-3s through food and, when necessary, supplementation can help individuals meet their health needs. As always, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen to ensure safety and efficacy tailored to individual health circumstances.



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.